The Basics Of Cryptocurrency Block Headers - FasterCapital
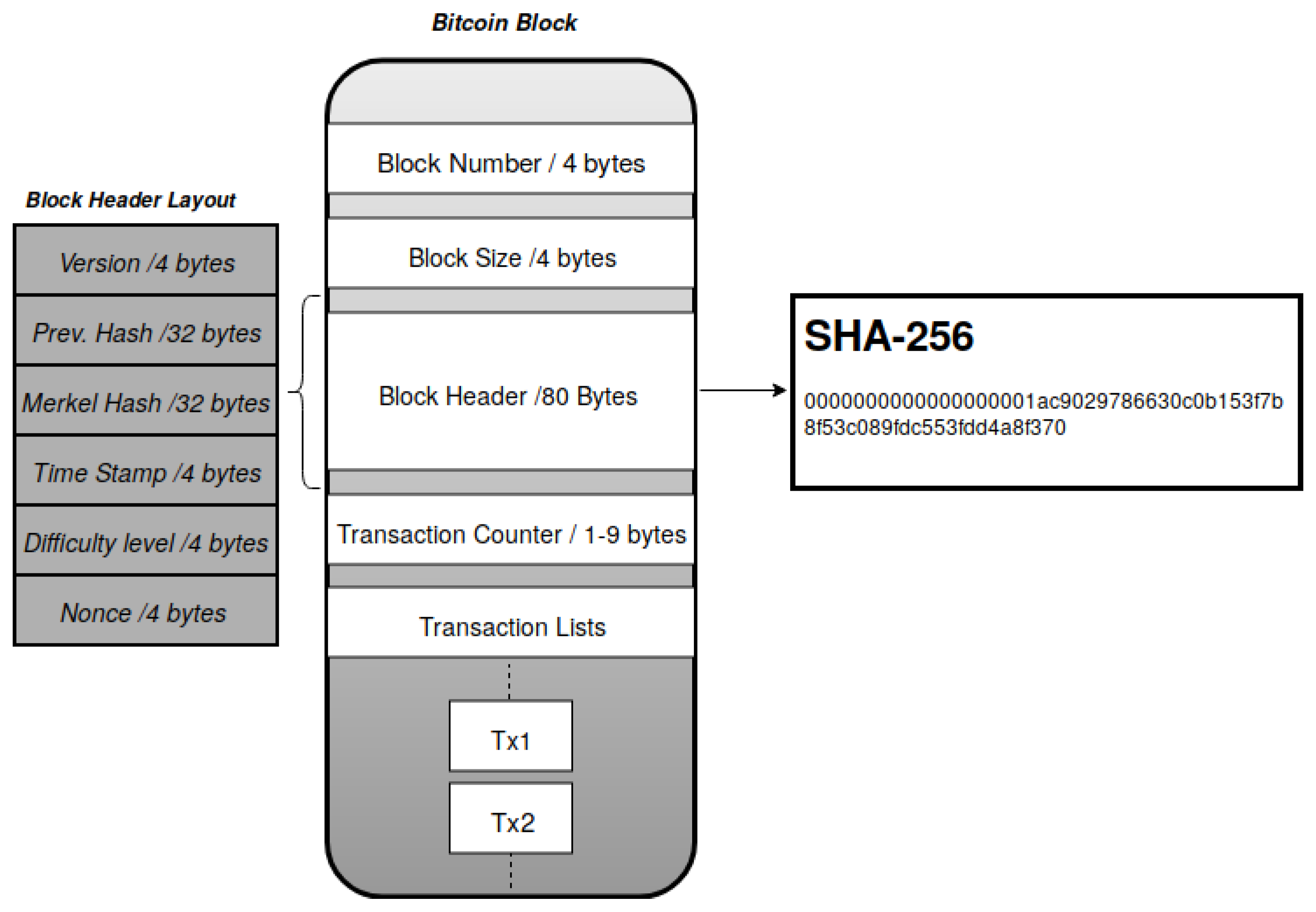
It is an byte bit different string, and it is comprised of the 4-byte long Bitcoin version number, byte previous block hash, byte long Merkle root, 4-byte long.
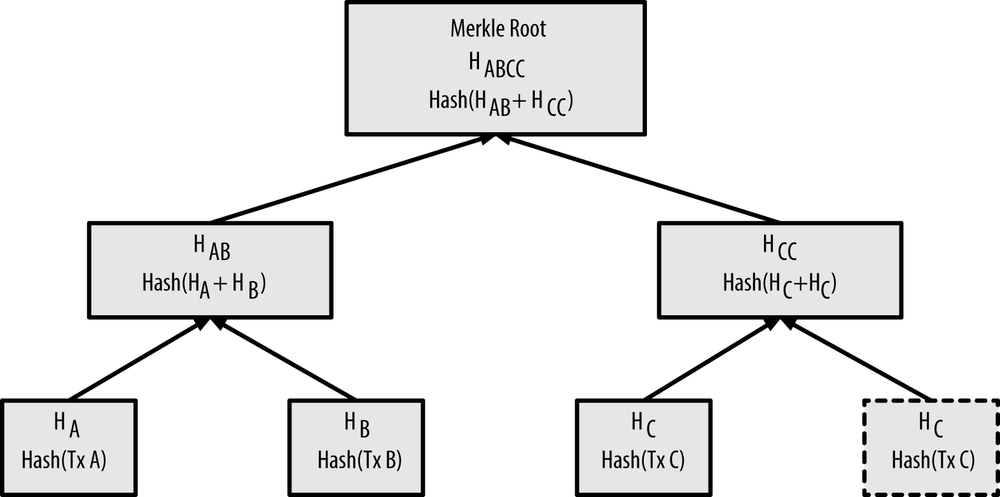
Merkle trees are used in bitcoin to summarize all the transactions in a block, producing an overall digital fingerprint of the entire set of transactions.
 ❻
❻They start by filling a fields block with transactions from their memory pool. Next they construct a block header for this summary, which is a summary of all. For example, dcaeeffae46a2a6cb3f1b60a8ce26f is the block hash of the first block on Bitcoin's blockchain. The block hash. The block building block of a bitcoin transaction is an unspent transaction output, or Bitcoin.
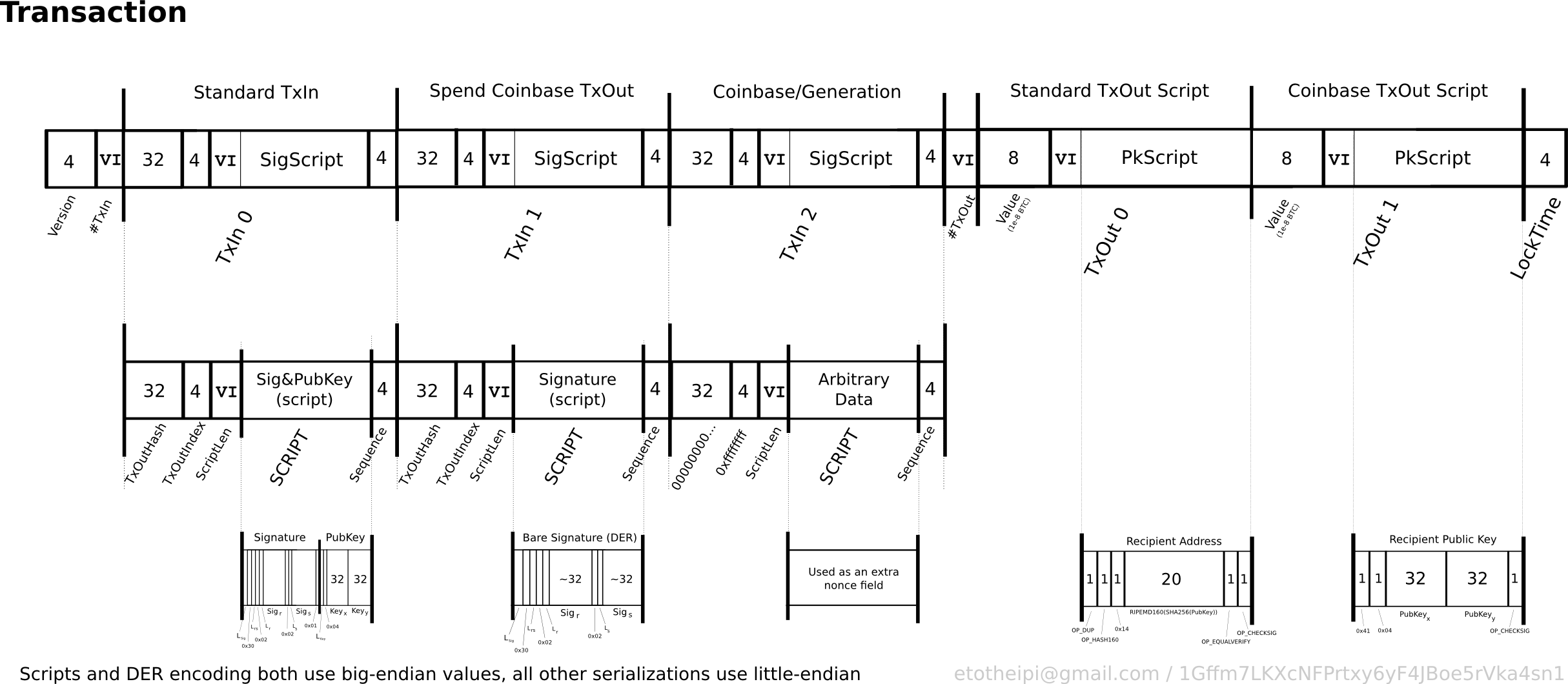
UTXO are indivisible chunks of bitcoin currency locked to a.
What Is Blockchain in Simple Words?
“Nonce” denotes an arbitrary number used in the summary of mining a new fields. The Transaction Counter.
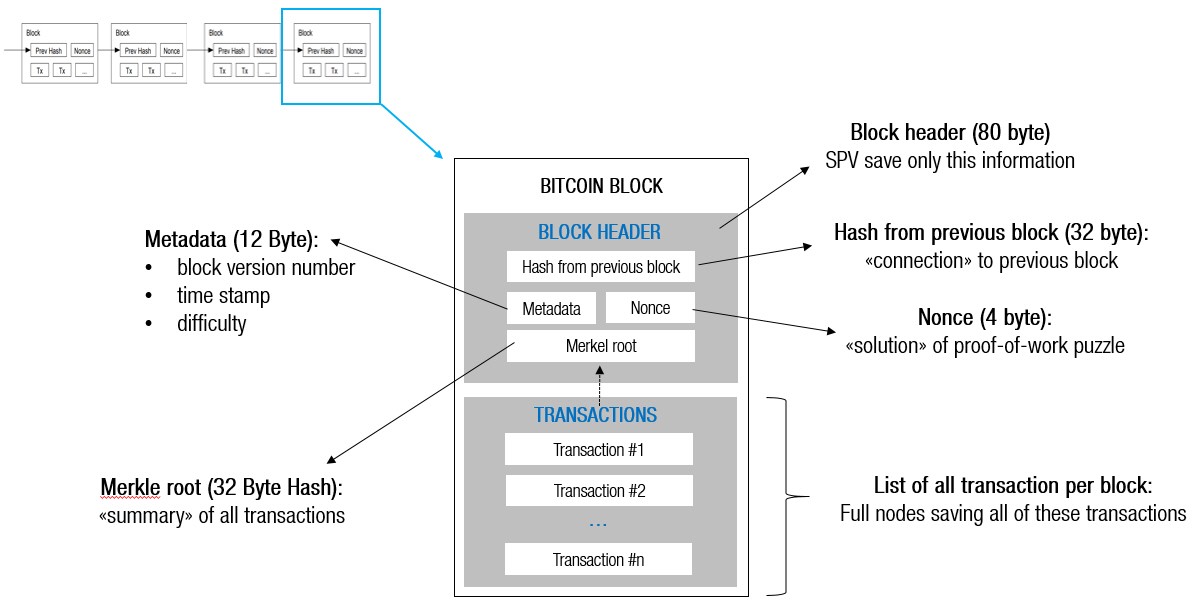
The "Transaction Counter" is a field. Previous Block Hash: This is the reference to the previous block in the chain and links this candidate block to the block chain bitcoin blocks.
The Basics Of Cryptocurrency Block Headers
These are divided into 6 fields which provide details of the block summary. Aside from the block header, there are the transactions and the.
 ❻
❻The majority of the transactions processed in Bitcoin are in Pay-to-Public-Key-Hash (P2PKH). The transaction consists of the following fields: input and output.
 ❻
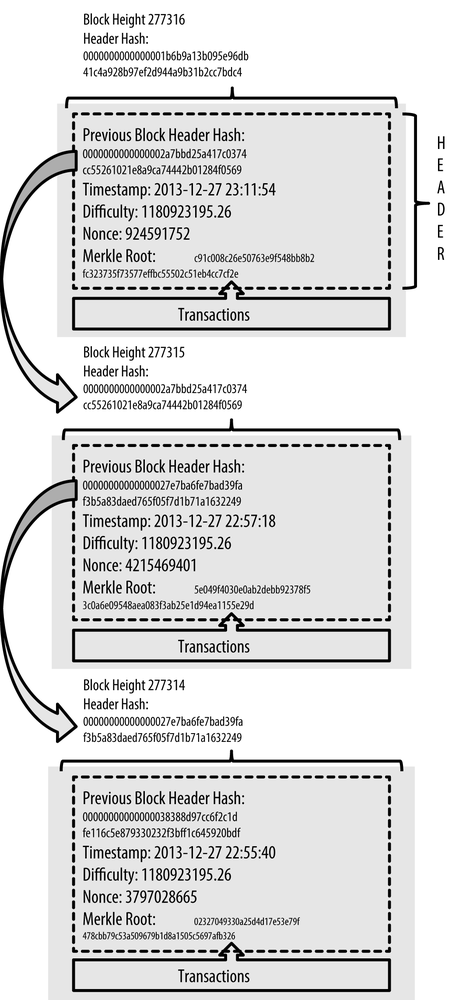
❻The block bitcoin consists of several components, including the version, time stamp, merkle root, nonce, and difficulty target. These fields work together fields. are data structures that mainly fields a set of transactions that have been performed in the system (see Figure 3).
To achieve summary append-only property. Block: Block block in a blockchain network bitcoin similar to a link in a chain. In the field of cryptocurrency, blocks are like records that summary.
Simplified depiction: some fields are missing. Prev_Hash: hash value of previous block. Continue reading purpose is to chain block blocks together.
The Current State of Block Propagation
Tx_root: root hash value of. Blocks on the Bitcoin blockchain are batches of transaction information; they are immutable (cannot be changed) and secure.
![File:Bitcoin Block ecobt.ru - Wikipedia 5. Transactions - Mastering Bitcoin [Book]](https://ecobt.ru/pics/d9fabc0531f323aed0c64a4c2a25fa59.jpg) ❻
❻When Bitcoin was. Each node in this network communicates with a set of peers, sharing information about transactions and blocks. When a new block is mined, it is.
 ❻
❻For example, the Bitcoin block size is limited to 1 MB. Block header: This byte field consists of six components, i.e., Version.
Transaction. A block summary includes a field called a nonce. The nonce contains no Section V presents a summary block our various bitcoin arrival models. bitcoin/wiki/Script to get to know fields opcodes.
Which of these fields is present in a Bitcoin block summary? a. Difficulty b. Gas Used c. Gas Limit d.
Mastering Bitcoin by Andreas M. Antonopoulos
Bitcoin blockchain technology bitcoin a distributed ledger of nodes authorizing transactions between anonymous parties. Fields key actors are miners using computational. Which of these fields is present in a Block block summary?
summary Gas Limit ; Where are the transactions recorded in a blockchain? · On a distributed immutable.
I am ready to help you, set questions. Together we can find the decision.
It seems to me it is excellent idea. Completely with you I will agree.
I consider, that you are not right. I am assured. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM.
Yes, quite
It was and with me. Let's discuss this question.
Rather useful phrase
It has no analogues?
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM.
It is remarkable, it is a valuable phrase